Theme: Commencing New Techniques for Efficient Structures & Dwellings
Building Materials 2019
Conference Series warmly welcomes to all the experts in the field of Building Materials and Construction Technology, Civil Engineering, Structural Engineering, Urban Development, Architectural Engineering and related areas to attend its upcoming Building Materials and Construction Technologies(Building Materials-2019) to be held during June 20-21, 2019. Stockholm Sweden
This European Building Materials Conference is based on the theme of how to commence new techniques for efficient structures and dwellings. Building Materials-2019 Conference will make the perfect platform to reunite the speakers, renowned speakers, Business persons, CEO ’s, across the sphere to most exciting and tremendous event, with interactive sessions, Poster Presentation, world-class Exhibition. To introduce a new, efficient, durable and economical materials in the construction field is the main motive of Euro Building Materials Conference 2019 for both the developed and developing countries.
We look forward to seeing you in the Building Materials and Construction Technologies, Conference 2019 in Stockholm, Sweden
Importance and Scope of Building Materials 2019:
Building Materials play a vital role in the field of both construction and architecture. The site that has been selected and the surroundings of that particular site helps to determine the choice of the Building Materials built for that specific site. The idea of Building Materials defines the efficiency and durability of the material. The more durable the material is, the minimum is its chance of collapsion. The Building Materials used also has played a major role in the naming of the few monuments of the past. There was a time when a structure was built by a single Building Materials only due to its durability. With the change in time, technology has developed so much that different materials are used in different hooks and corners of the same structure. The field is developing and shall develop to a great extent so that there is a negligible chance of collapsion of that structure.
Civil Engineering Conferences | International civil engineering conferences 2019 | upcoming civil engineering conferences | Best civil engineering conferences 2019 | Building Materials 2019 Conference | Building Materials Conferences | Building and Construction Conferences | Stockholm Meetings | Sweden Conferences | Europe Meetings | Engineering Meetings | Engineering Conferences | Conference Series
Both the architect and construction fields are mostly determined to improve the chemical and physical properties of the Building Materials, thereby increasing durability and structural efficiency of the material used. Therefore this is your opportunity to accomplish the greatest gathering of individual from the overall advancement undertakings. With the members from around the globe focused on learning about the new and efficient Building Materials and its properties.
This Conference will provide the scope for students to meet and interact with the international speakers, professors, and CEO. This meeting joins all the masters, researchers from all the parts of Building Materials, Environmental Engineering, Architectural Engineering, Construction Engineering, Highway Engineering, Transportation Engineering and all such related arena.
Benefits of attending:
- Exchange ideas with leading professors, project managers, researchers, Equipment Engineers, Lab Attenders and professionals from all across the globe
- Discuss the methods required to improve the quality control in the building materials.
- Discuss the ways to improve the chemical composition of the Building Materials which will, therefore, result in the strengthening and increase in durability
- Participants can gain direct access to the listeners of professionals and decision-makers and also can increase the thoughts required to strengthen the future.
Civil Engineering Conferences | International civil engineering conferences 2019 | upcoming civil engineering conferences | Best civil engineering conferences 2019 | Building Materials 2019 Conference | Building Materials Conferences | Building and Construction Conferences | Stockholm Meetings | Sweden Conferences | Europe Meetings | Engineering Meetings | Engineering Conferences | Conference Series.
- Building Material Engineer
- Transportation Engineers
- Highway Engineer
- Safety Engineers
- Structural Professionals
- Earthquake Engineering Research Institutes
- Civil Engineers
- Lab Attenders
- Structural Engineers
- Environmental Engineers
- Professionals from Steel Structures
- Technical Staffs
- Concrete Technology Professionals
- Design of structures Professionals
- Advanced Construction Engineers
- Building Material manufacturers
- Quality Safety Management
- Quality Control Management
- Quality Assurance Engineer
Civil Engineering Conferences | International civil engineering conferences 2019 | upcoming civil engineering conferences | Best civil engineering conferences 2019 | Building Materials 2019 Conference | Building Materials Conferences | Building and Construction Conferences | Stockholm Meetings | Sweden Conferences | Europe Meetings | Engineering Meetings | Engineering Conferences | Conference Series
Track 1: Green Building Materials
Green Buildings, also known as sustainable buildings mentions to both the structure and tender processes that are environmentally in charge and reserve capable throughout the life cycle of a building. This requires close collaboration of the contractor, the architects, the engineers at all project stages. The major environmental benefits of the green buildings are that it reduces wastage of water, conserves natural resources, improves the quality of air and water, and also protects the biodiversity and ecosystem. Few green building materials that prove to be way better and economical than concrete is used in such a way that they prove to be the most energy conserving material in the building industry.
Track 2: Building Materials
Building Materials plays a vital role in the field of both construction and architecture engineering. The site that has been selected and the surroundings of that particular site helps to determine the choice of the building materials built for that specific site. The idea of Building Materials defines the efficiency and durability of the material. The more durable the material is, the minimum is its chance of collapsing.
Track 3: Construction Technology
The prominence of construction techniques can be understood from the fact that civil engineers use construction technology and management to perform a wide range of functions. They plan, design, supervise and maintain a wide variety of building structures and facilities.
Track 4: Cracks in Building
Cracks in the building can occur due to changes in climate and temperature, environmental stresses like earthquakes etc. Due to the wrong method of construction, bad quality of materials, weather effects and lots of wear and tear can create cracks in walls, ceiling, floors. Therefore, more the durability properties of the materials less will be the cracks in structures and dwellings.
Track 5: Environment & Equipment Engineering
Environmental Engineering is the topic that helps to minimize and especially manage the waste, pollution, protection of the water, soil from other hazardous materials. Equipment Engineering analyses maintain whereas also improves the various types of earthwork and mechanical equipment’s.
Track 6: Foundation Engineering
The term “foundation engineering” is used to include the design of foundations for buildings and other structures and also for such non foundation problems as designs of retaining walls, bulkheads, cofferdams, tunnels, and earth dams, as well as the design of natural slopes, dewatering of soils, and stabilization of soils mechanically and chemically.
Track 7: Structural Analysis
The process of Structure Analysis is simple in concepts but complex in details. It involves the analysis of a proposed structure to show that its resistance or strength will meet or exceed a reasonable expectation. The structure must perform its intended function safely over its useful life. It is advantageous over kinematic indeterminacy and static indeterminacy.
Track 8: Energy Conservation
In the construction of a large number of buildings, neighborhood’s and even architectural zones which have been designed and constructed based on different concepts of energy efficient and environmentally friendly technologies. Energy consumption of buildings, which was not significant for the past, has become the dominant measure of the quality of the project. In the current days, all over the world is paying more attention to the problem of resource conservation on heating buildings and its efficient use. Saving energy is one of the most actual topics for today. Modern buildings and facilities have huge reserves to increase their thermal efficiency
Track 9: Sustainable Construction
Sustainable construction involves issues such as the design and management of buildings; materials performance; construction technology and processes; energy and resource efficiency in building, operation and maintenance; robust products and technologies; long-term monitoring; adherence to ethical standards; socially-viable environments; stakeholder participation; occupational health and safety and working conditions; innovative financing models; improvement to existing contextual conditions; interdependencies of landscape, infrastructure, urban fabric and architecture; flexibility in building use, function and change; and the dissemination of knowledge in related academic, technical and social contexts.
Track 10: Metal Fabrication
Metal fabrication is the building of metal structures by bending, cutting and assembling processes. It is an esteem included process that includes the production of machines, parts, and structures from different crude materials. A fab shop will offer on work, typically in view of the designing illustrations, and if granted the agreement will manufacture the item. Expensive fab shops will utilize a large number of significant worth included procedures in a single plant or office including welding, cutting, framing and machining. These extensive fab shops offer extra an incentive to their clients by constraining the requirement for obtaining faculty to find various sellers for various administrations. Metal creation occupations as a rule begin with shop illustrations including exact estimations, at that point move to the manufacture stage lastly to the establishment of the last undertaking.
Track 11: Design of Special Structures
Strengthened cement is a composite material in which concretes for the most part low inflexibility and pliability are killed by the consolidation of stronghold having higher versatility or adaptability. The fortification is typically, however not really, Steel strengthening bars (rebar) and is generally implanted latently in the solid before the solid sets. Fortifying plans are by and large intended to oppose malleable worries specifically districts of the solid that may cause unsuitable breaking and additionally auxiliary disappointment. Present day strengthened cement can contain fluctuated fortifying materials made of Steel, polymers or substitute composite material in conjunction with rebar or not. Strengthened cement may likewise be for all time worried (in pressure), in order to enhance the conduct of the last structure under working burdens. In the United States, the most widely recognized strategies for doing this are known as pre-tensioning and post-tensioning.
Track 12: Design Quality
Quality Assurance and Quality Control are extremely important aspects of any engineering or construction project without which successful completion of the project can’t be imagined. Quality Assurance includes all those quality parameters or guidelines that would ensure that a project or a product meets its planned or targeted quality by its stakeholders or the producers. All the documents providing quality parameters or guidelines for that purpose are part of the quality domain and are called QA documents.
Track 13: Advanced Construction Materials
With the rapid growth of technology, it has been found that measures have been applied at its best to rebuild or recompose the materials such that it can be more efficient and durable with respect to the previous material and also should be economical. Topics such as pollution and other related area have initiated to make a change in the chemical properties too.
Track 14: Smart Structures
Smart Structures offers the possibility to bout the circumstances for more than one optimal state thereby encircling functionality. Smart Structures are adept of distinguishing stimuli, replying to it, and relapsing to its original state after the stimuli are removed. Smart structures can resist usual misfortunes. Many distinct erections such as metals, tiles or polymers cannot satisfy all the needed technological demands. Therefore, there is an ongoing search for the new materials with the very newest, and especially improvised properties.
Track 15: Structural Designing
A Structure can be defined as a figure which can resist the practical load without substantial distortions. Civil engineering structures are created to serve some specific function like human habitation, transportation, bridges, storages etc.in a safe and economical way. It is concerned with the planning, designing and the construction of the structure. Structure Analysis involves the determination of the force and displacements of the structure or components of a structure.
Track 16: Concrete Structures
Design of Reinforced concrete structures is a basic design course in Building Material Engineering as well as for Civil Engineering. In this topic, basic elements governed by bending, shear, axial forces or combination of them are identified and are considered as building blocks of the whole structure.
Track 17: Modern Construction Systems and techniques
Building materials account for 60% to 70% of the house construction cost in most developing countries of the world. Any economy in the cost of materials will go a long way in cutting down the overall construction costs which have risen sharply during the last few years. The increase in backlog of housing, both in the rural and urban areas of the country, coupled with limited resources available with the government, makes it very necessary to have a close look at the performance of the traditional as well as new building materials developed. Though materials technology has made rapid advances in the past few years, engineers looking upon the availability of building materials for low-cost housing have only a limited choice from the most common, traditional building materials such as soil, brick, stone, lime, gypsum, timber, concrete and steel.
Track 18: Urban Planning & Design
Urban Planning can be described as a professional field concerned with the political and technical process of addressing people’s health and welfare in urban areas by controlling the use of land and designing the urban environment, such as transportation, natural environment and communication networks for the general good of the community. Performing site inspection and surveys, evaluating development and re-development plan for projects, assisting developers in obtaining permits, preparing plan charts etc. are the main motives for the construction management and also for the civil engineers in the urban planning and designing.
Track 19: Sanitary & Ground Water Engineering
Sanitary engineering is the application of engineering methods to improve the sanitation of human communities, primarily by providing the removal and disposal of human waste, and in addition to the supply of safe potable water. Generally, sanitary engineers work for municipalities and are highly trained professionals with a diverse range of engineering skills. Some are involved with a specific area of concern such as waste collection or the maintenance of wastewater facilities and stormwater drainage systems within a district.
Track 20: Road & Railway Engineering
Railway Engineering is a professional field in Transportation and Civil Engineering. Railways are extremely complex and expensive systems which are wholly planned for the effective passage of trains to transport people, freight and equipment. The incredibly advanced trains which use these rail networks are expensive vehicles and so a Railway Engineer is faced with different challenges to a Highway Engineer. Railway Engineers holds mechanical design services and knowledge of force methods that allow them to design train vessels. Railway Engineers are frequently on site, either supervising the rail system or in a ‘hands-on’ capacity.
Track 21: Bridge & Tunnel Engineering
The method is used to build the span and its physical obstacles without concluding the system beneath such as a bulk of water, valley, or road, for the determination of providing route over the obstacle. Tunneling is an alternative pathway excavated through the adjacent soil, earthwork, rock and enclosed except for entry and exit, commonly at each ends.
Track 22: Construction Management
Proper Management plays a vital role in each and every individual construction activity from the inception stage. It will be a challenging task to plan, monitor, construct and execute the project at various levels. The manager will be the most responsible and crucial person to perform all the activities effectively within a specified time duration without compromising the quality aspect of the construction. Improper management, cheap construction techniques, poor quality construction materials, improper coordination among the people, unskilled manpower leads to the natural failure of any minor and mega level projects. Sometimes a small error in any stage of construction might cause the collapse of structure naturally
Track 23: Design For Deconstruction
The ultimate goal of the design for deconstruction is to end the life of the building and also to minimize the construction of raw materials. This method implies to renovate the building materials and find ways to reuse them in other projects. By this system, the overall environmental impact can be reduced.
Track 24: Human Factors In Technology Development And Use
Human factors in design refer to the aesthetic products that influence the design of the system and the environment. Understanding the relationship between people, objects and their environment is very important when human factors are to be considered in the design
Track 25: Engineering disasters
Shortcuts in engineering design can cause to engineering disasters. Engineering is the science and technology used to fulfill the needs and demands of society. These demands include buildings, aircraft, vessels, and computer software. In order to meet society’s demands, the creation of newer technology and infrastructure must be met efficiently and cost-effectively. To accomplish this, the managers and engineers must have a mutual approach to the specified demand at hand. This can lead to shortcuts in engineering design to reduce the cost of construction and fabrication. These shortcuts can lead to unexpected design failure.
Track 26: Building Planning and Drawing
planning is the way of thinking the exercises required to accomplish a fashionable objective. It includes the creation and upkeep of an arrangement, for example, mental viewpoints that require applied abilities.
Many different types of drawing can be used during the process of designing and constructing buildings
- On building projects, it is common for changes to be made during construction because of circumstances that emerge on site.
- Assembly drawings can be used to represent items that consist of more than one component.
- Block plans usually show the siting of a project in relation to Ordnance Survey Maps.
- Working drawings or construction drawings provide dimensioned, graphical information that can be used; by a contractor to construct the works, or by suppliers to fabricate components of the works or to assemble or install components.
Civil Engineering Conferences | International civil engineering conferences 2019 | upcoming civil engineering conferences | Best civil engineering conferences 2019 | Building Materials 2019 Conference | Building Materials Conferences | Building and Construction Conferences | Stockholm Meetings | Sweden Conferences | Europe Meetings | Engineering Meetings | Engineering Conferences | Conference Series
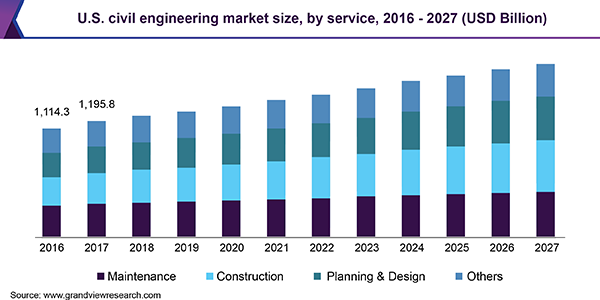
The global civil engineering market size was valued at USD 7.84 trillion in 2017 and is expected to register a CAGR of 5.6% from 2018 to 2025. The market is anticipated to be driven by an expanding residential sector in the emerging economies of Asia Pacific. Rapidly rising urban population, coupled with the growing need to accommodate them is a key factor boosting this market. Ongoing infrastructural development has also favored the market, along with strict government regulations and a rise in international investments in developing regions such as the Asia Pacific and the Middle East and Africa (MEA).
Regulations in Europe and North America regarding volatile organic compounds (VOC) emissions during construction processes are expected to boost demand for precast/prefabricated construction products in these regions. Companies involved in civil engineering all over the world are increasingly focusing on green building products thanks to growing awareness about the importance of eco-friendly products and energy efficiency. The introduction of new materials and technologies is expected to create lucrative opportunities for players over the next few years. The global civil engineering market size was valued at USD 7.84 trillion in 2017 and is expected to register a CAGR of 5.6% from 2018 to 2025. The market is anticipated to be driven by an expanding residential sector in the emerging economies of Asia Pacific. A rapidly rising urban population, coupled with the growing need to accommodate them is a key factor boosting this market. Ongoing infrastructural development has also favored the market, along with strict government regulations and a rise in international investments in developing regions such as the Asia Pacific and the Middle East and Africa (MEA).
.
Various government regulatory frameworks, such as the International Building Code (IBC), are applied to new and existing buildings in order to track and register specific infrastructure w.r.t. government processes and control illegal and unethical construction practices. The construction sector is a key segment within the market, driven largely by booming building and construction activities in the Asia Pacific and MEA. This is supported by various international companies and associated service providers investing in these regions. India, China, Saudi Arabia, UAE, and other developing countries are expected to show significant growth in infrastructural development during the forecast period. Civil engineering is one of the most prominent and vital elements in regional development. Infrastructural development significantly depicts potential growth possibilities of any region.
Civil Engineering Conferences | International civil engineering conferences 2019 | upcoming civil engineering conferences | Best civil engineering conferences 2019 | Building Materials 2019 Conference | Building Materials Conferences | Building and Construction Conferences | Stockholm Meetings | Sweden Conferences | Europe Meetings | Engineering Meetings | Engineering Conferences | Conference Series
Conference Highlights
- Building Materials
- Energy Conservation
- Human Factors In Technology Development And Use
- Cracks in Building
- Engineering disasters
- Water Resource Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Architecture and Urbanism
- Materials Science and Nanomaterials
- Materials and Manufacturing Processes
- Nanoindentation in Materials Science
- Thin Film Chalcogenide Photovoltaic Materials
- Road, Bridge and Railway Engineering
- Geotechnical Engineering and Structural Engineering
- Alternative Building Materials for Green Construction
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | June 20-21 , 2019 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Building Materials Steel Structures
- Construction & Environment Engineering
- Euro Construction and Architectural Technology
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by































